The Philippines has a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall throughout the year. The country experiences two main seasons: the wet season (or rainy season) and the dry season. Here are some key features of the climate in the Philippines:
Wet Season: The wet season generally occurs from June to November. During this period, the country experiences frequent rainfall, tropical storms, and typhoons (known as hurricanes or cyclones in other parts of the world). The wet season is characterized by high humidity and cloudy skies, with the peak of typhoon activity typically happening between July and October.
Dry Season: The dry season usually spans from December to May. It is characterized by relatively lower rainfall and higher temperatures. The months of March to May are the hottest, with temperatures often reaching their peak during this period. However, even during the dry season, some regions may experience occasional rain showers or thunderstorms.
Temperature: The temperature in the Philippines remains relatively high throughout the year, with little variation between seasons. Average temperatures range from 25 to 32 degrees Celsius (77 to 90 degrees Fahrenheit). Coastal areas and low-lying regions tend to have slightly higher temperatures compared to higher elevated areas.
Humidity: The Philippines has a high level of humidity due to its tropical location and proximity to bodies of water. Humidity levels can range from 70% to 85% on average, making the air feel moist and sticky.
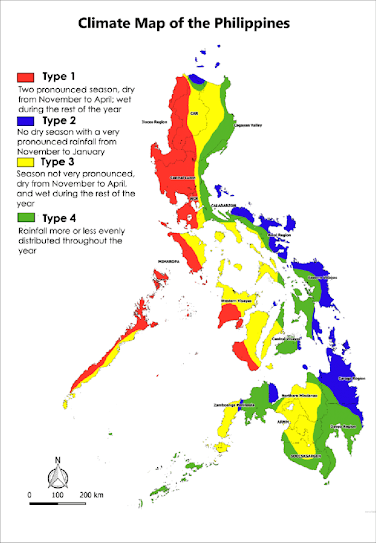
Regional Variation: The climate in the Philippines can vary across different regions due to factors such as topography, proximity to the coast, and prevailing wind patterns. Regions in the northern part of the country generally experience cooler temperatures compared to those in the southern parts. Mountainous areas, such as the Cordillera region and parts of Mindanao, have cooler climates due to their higher elevations.
Monsoon Seasons: The Philippines experiences two monsoon seasons: the southwest monsoon (Habagat) and the northeast monsoon (Amihan). The southwest monsoon occurs from June to October and brings heavy rainfall, while the northeast monsoon, from November to February, brings cooler and drier winds.
It's important to note that climate patterns can be subject to variations and changes from year to year due to natural climate phenomena, such as El Niño and La Niña. Additionally, different regions within the Philippines may have microclimates with unique weather patterns influenced by local geography and environmental factors.

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario